这是我自学 MIT6.S081 操作系统课程的 lab 代码笔记第九篇:File System。此 lab 大致耗时:4小时。
课程地址:https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.S081/2020/schedule.html
Lab 地址:https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.S081/2020/labs/fs.html
我的代码地址:https://github.com/Miigon/my-xv6-labs-2020/tree/fs
Commits: https://github.com/Miigon/my-xv6-labs-2020/commits/fs本文中代码注释是编写博客的时候加入的,原仓库中的代码可能缺乏注释或代码不完全相同。
Lab 9: File Systems
为 xv6 的文件系统添加大文件以及符号链接支持。该 lab 难度较低。
Large files (moderate)
原理与分析
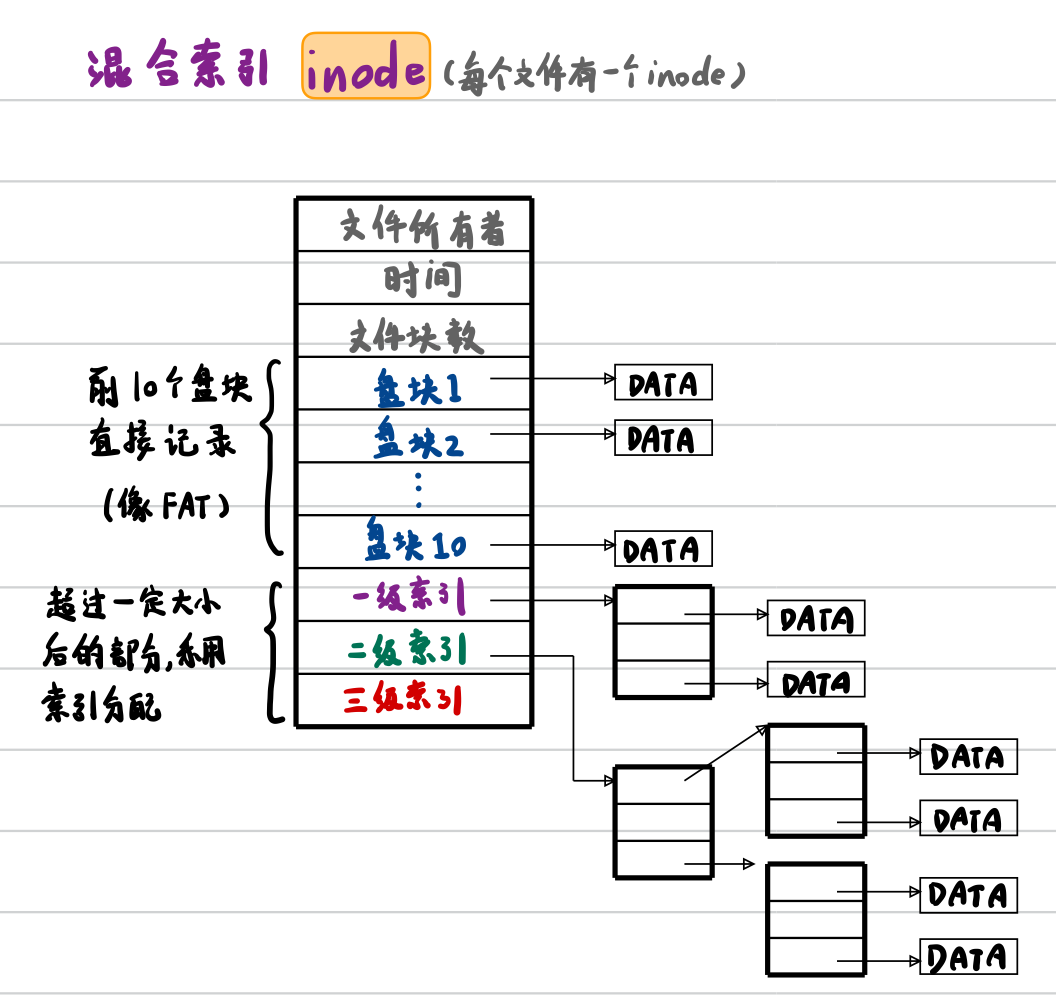
与 FAT 文件系统类似,xv6 文件系统中的每一个 inode 结构体中,采用了混合索引的方式记录数据的所在具体盘块号。每个文件所占用的前 12 个盘块的盘块号是直接记录在 inode 中的(每个盘块 1024 字节),所以对于任何文件的前 12 KB 数据,都可以通过访问 inode 直接得到盘块号。这一部分称为直接记录盘块。
对于大于 12 个盘块的文件,大于 12 个盘块的部分,会分配一个额外的一级索引表(一盘块大小,1024Byte),用于存储这部分数据的所在盘块号。
由于一级索引表可以包含 BSIZE(1024) / 4 = 256 个盘块号,加上 inode 中的 12 个盘块号,一个文件最多可以使用 12+256 = 268 个盘块,也就是 268KB。
inode 结构(含有 NDIRECT=12 个直接记录盘块,还有一个一级索引盘块,后者又可额外包含 256 个盘块号):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// kernel/fs.c
// note: NDIRECT=12
// On-disk inode structure
struct dinode {
short type; // File type
short major; // Major device number (T_DEVICE only)
short minor; // Minor device number (T_DEVICE only)
short nlink; // Number of links to inode in file system
uint size; // Size of file (bytes)
uint addrs[NDIRECT+1]; // Data block addresses
};
本 lab 的目标是通过为混合索引机制添加二级索引页,来扩大能够支持的最大文件大小。
这里祭出上学校 OS 课的时候的笔记图:
本 lab 比较简单,主要前置是需要对文件系统的理解,确保充分理解 xv6 book 中的 file system 相关部分。
代码实现
首先修改 struct inode(内存中的 inode 副本结构体)以及 struct dinode(磁盘上的 inode 结构体),将 NDIRECT 直接索引的盘块号减少 1,腾出 inode 中的空间来存储二级索引的索引表盘块号。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// kernel/fs.h
#define NDIRECT 11 // 12 -> 11
#define NINDIRECT (BSIZE / sizeof(uint))
#define MAXFILE (NDIRECT + NINDIRECT + NINDIRECT * NINDIRECT)
// On-disk inode structure
struct dinode {
short type; // File type
short major; // Major device number (T_DEVICE only)
short minor; // Minor device number (T_DEVICE only)
short nlink; // Number of links to inode in file system
uint size; // Size of file (bytes)
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2]; // Data block addresses (NDIRECT+1 -> NDIRECT+2)
};
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
// kernel/file.h
// in-memory copy of an inode
struct inode {
uint dev; // Device number
uint inum; // Inode number
int ref; // Reference count
struct sleeplock lock; // protects everything below here
int valid; // inode has been read from disk?
short type; // copy of disk inode
short major;
short minor;
short nlink;
uint size;
uint addrs[NDIRECT+2]; // NDIRECT+1 -> NDIRECT+2
};
修改 bmap(获取 inode 中第 bn 个块的块号)和 itrunc(释放该 inode 所使用的所有数据块),让其能够识别二级索引。(基本上和复制粘贴一致,只是在查出一级块号后,需将一级块中的数据读入,然后再次查询)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
// kernel/fs.c
// Return the disk block address of the nth block in inode ip.
// If there is no such block, bmap allocates one.
static uint
bmap(struct inode *ip, uint bn)
{
uint addr, *a;
struct buf *bp;
if(bn < NDIRECT){
if((addr = ip->addrs[bn]) == 0)
ip->addrs[bn] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
return addr;
}
bn -= NDIRECT;
if(bn < NINDIRECT){ // singly-indirect
// Load indirect block, allocating if necessary.
if((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT]) == 0)
ip->addrs[NDIRECT] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if((addr = a[bn]) == 0){
a[bn] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
return addr;
}
bn -= NINDIRECT;
if(bn < NINDIRECT * NINDIRECT) { // doubly-indirect
// Load indirect block, allocating if necessary.
if((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1]) == 0)
ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if((addr = a[bn/NINDIRECT]) == 0){
a[bn/NINDIRECT] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
bn %= NINDIRECT;
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if((addr = a[bn]) == 0){
a[bn] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
return addr;
}
panic("bmap: out of range");
}
// Truncate inode (discard contents).
// Caller must hold ip->lock.
void
itrunc(struct inode *ip)
{
int i, j;
struct buf *bp;
uint *a;
for(i = 0; i < NDIRECT; i++){
if(ip->addrs[i]){
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[i]);
ip->addrs[i] = 0;
}
}
if(ip->addrs[NDIRECT]){
bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT]);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
for(j = 0; j < NINDIRECT; j++){
if(a[j])
bfree(ip->dev, a[j]);
}
brelse(bp);
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT]);
ip->addrs[NDIRECT] = 0;
}
if(ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1]){
bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1]);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
for(j = 0; j < NINDIRECT; j++){
if(a[j]) {
struct buf *bp2 = bread(ip->dev, a[j]);
uint *a2 = (uint*)bp2->data;
for(int k = 0; k < NINDIRECT; k++){
if(a2[k])
bfree(ip->dev, a2[k]);
}
brelse(bp2);
bfree(ip->dev, a[j]);
}
}
brelse(bp);
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT+1]);
ip->addrs[NDIRECT + 1] = 0;
}
ip->size = 0;
iupdate(ip);
}
运行结果
1
2
3
4
$ bigfile
..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
wrote 65803 blocks
bigfile done; ok
Symbolic links (moderate)
实现符号链接机制。
代码实现
首先实现 symlink 系统调用,用于创建符号链接。 符号链接与普通的文件一样,需要占用 inode 块。这里使用 inode 中的第一个 direct-mapped 块(1024字节)来存储符号链接指向的文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
// kernel/sysfile.c
uint64
sys_symlink(void)
{
struct inode *ip;
char target[MAXPATH], path[MAXPATH];
if(argstr(0, target, MAXPATH) < 0 || argstr(1, path, MAXPATH) < 0)
return -1;
begin_op();
ip = create(path, T_SYMLINK, 0, 0);
if(ip == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
// use the first data block to store target path.
if(writei(ip, 0, (uint64)target, 0, strlen(target)) < 0) {
end_op();
return -1;
}
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return 0;
}
在 fcntl.h 中补齐 O_NOFOLLOW 的定义:
1
2
3
4
5
6
#define O_RDONLY 0x000
#define O_WRONLY 0x001
#define O_RDWR 0x002
#define O_CREATE 0x200
#define O_TRUNC 0x400
#define O_NOFOLLOW 0x800
修改 sys_open,使其在遇到符号链接的时候,可以递归跟随符号链接,直到跟随到非符号链接的 inode 为止。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
uint64
sys_open(void)
{
char path[MAXPATH];
int fd, omode;
struct file *f;
struct inode *ip;
int n;
if((n = argstr(0, path, MAXPATH)) < 0 || argint(1, &omode) < 0)
return -1;
begin_op();
if(omode & O_CREATE){
ip = create(path, T_FILE, 0, 0);
if(ip == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
} else {
int symlink_depth = 0;
while(1) { // recursively follow symlinks
if((ip = namei(path)) == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
ilock(ip);
if(ip->type == T_SYMLINK && (omode & O_NOFOLLOW) == 0) {
if(++symlink_depth > 10) {
// too many layer of symlinks, might be a loop
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
if(readi(ip, 0, (uint64)path, 0, MAXPATH) < 0) {
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
iunlockput(ip);
} else {
break;
}
}
if(ip->type == T_DIR && omode != O_RDONLY){
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
}
// .......
iunlock(ip);
end_op();
return fd;
}
运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
$ symlinktest
Start: test symlinks
test symlinks: ok
Start: test concurrent symlinks
test concurrent symlinks: ok